Some traders may unconsciously commit arbitrage, an act prohibited by many FX brokers. So this article introduces the overview of arbitrage and clarifies what act falls under it.
[Summary of this article].
- Arbitrage is an act of trading which utilizes the price differences between the markets with the different rules to make a profit.
- The difference between cross order and arbitrage depends on whether the risk of exchange loss is excluded.
- Many brokers prohibit arbitrage because it puts the broker at an unfair disadvantage.
- Traders committing arbitrage typically utilize bonuses, Negative Balance Protection and swap point.
Many people would not be willing to commit something illegal. What we should avoid is “unintentional” arbitrage. For example, after a trader did an act of trading, thinking that there was no illegality, it is later found arbitrage, and the broker imposes a stiff penalty for the trader.
It is worrisome that a trader holding multiple accounts is likely to commit unintentional arbitrage. I hope fewer traders can avoid such an act and the punishment by reading this article.
Contents
- 1 What Is Arbitrage?
- 2 What Is Different Between Arbitrage And Cross Order?
- 3 Which Trading Acts Are PROHIBITED as Arbitrage?
- 4 Arbitrage Taking Advantage of Bonus
- 5 Arbitrage Taking Advantage of Negative Balance Protection
- 6 Arbitrage Taking Advantage Of Swap Point
- 7 Penalty for Arbitrage
- 8 How Brokers Detect Arbitrage
- 9 Conclusion
What Is Arbitrage?
Arbitrage is an act of trading which utilizes the price differences between the markets with the different rules to make a profit.
When it comes to FX trading, arbitrage means a method of avoiding exchange losses with an intention to make profits.
Theoretically, arbitrage can generate profits. But in practice, traders can not make a profit from arbitrage. Since it puts the broker at an unfair disadvantage, many brokers prohibit arbitrage.
What Is Different Between Arbitrage And Cross Order?
Arbitrage and cross order have in common that a trader simultaneously has long and short positions within the same currency pair. In a broader sense, arbitrage is a type of cross order.
Cross Order
When a trader holds long and short positions within the same currency pair, it can be deemed "cross order.” There is no illegality in the cross order in the same account for the currency gain, and many brokers such as XM and HotForex allow it.
Related Article
【Cross Order】 Is Cross Order Prohibited? Overview of Cross Order – Benefit and Trading Method –
Arbitrage
When a trader holds long and short positions within the same currency pair, or over the highly-related currency pairs, with an intention to avoid the risk of exchange loss, it can be deemed “arbitrage.” In this case, bonuses, Negative Balance Protection and swap points are utilized.
As mentioned above, while the trader can “theoretically” make a profit by arbitrage, it puts brokers at a disadvantage. In general, placing a cross order with different accounts can be deemed arbitrage. In fact, many brokers such as XM and HotForex prohibit this act of trading.
Which Trading Acts Are PROHIBITED as Arbitrage?
There are mainly three acts of trading which fall under arbitrage.
- Arbitrage taking advantage of bonus
- Arbitrage taking advantage of Negative Balance Protection
- Arbitrage taking advantage of swap points
[NOTE]
THE ACTS MENTIONED BELOW ARE ALL PROHIBITED BY MANY BROKERS.
DO NOT USE THESE PROCEDURES. The following explanations are introduced as a reminder.
Arbitrage Taking Advantage of Bonus
1) Take advantage of the deposit bonus and use two different accounts (account A and account B)
2) Adjust the balance of each account as follows;
Account A: USD 1,000 as a deposit bonus + personally-owned USD 9,000
Account B: USD 0 as a deposit bonus + personally-owned USD 10,000
3) Place offsetting orders as A is used for a long position and B is used for a short position
(this falls under the cross order using the different accounts, which is prohibited by XM and HotForex).
4) The order of A posts a loss while the order of B generates enough profit to fill the loss. However, as the balance of A includes the bonus, the profit of B virtually surpasses the loss of A. The profit-and-loss margin turns plus.

Arbitrage Taking Advantage of Negative Balance Protection
1)A trader opens two accounts (Account A and Account B).
2)The trader deposits the same amount of margin to each account.
3)The trader places opposite-direction orders (ex. long position for Account A and short position for Account B). This falls under the cross order with multiple accounts, the act many brokers prohibit.
4)Due to a huge fluctuation, the trader loses money larger than the deposited margin in Account B. But at the same time, the trader can make a huge profit in Account A.
5)The balance of B goes negative on the books as the trader not only lost the entire margin but also incurred the debt. But the broker writes off the debt with Negative Balance Protection to make the negative balance zero.
6)The trader utilizes the profit of Account A to compensate for the lost margin of Account B.
7)As a result, the trader can secure a profit from the difference between the earned profit and the makeup amount.

Arbitrage Taking Advantage Of Swap Point
This arbitrage utilizes the difference of multiple brokers’ swap points.
[What Is Swap Point?]
Swap point is the interest spread calculated based on the interest rate of each currency. A trader can acquire swap point by selling a low-interest currency and purchasing a high-interest currency. In an opposite case, the trader is required to pay swap point. Many brokers settle swap points at the time of the date change.
1)A trader opens accounts in two brokers with a preferable difference in swap points for the same currency pair.
2)The trader places a cross order with the same lot size.
3)As a cross order has been placed for the same pair, the trader can earn profit without risks. For example, the difference between Broker A’s long swap and Broker B’s short swap turns positive, the trader can make a profit daily.
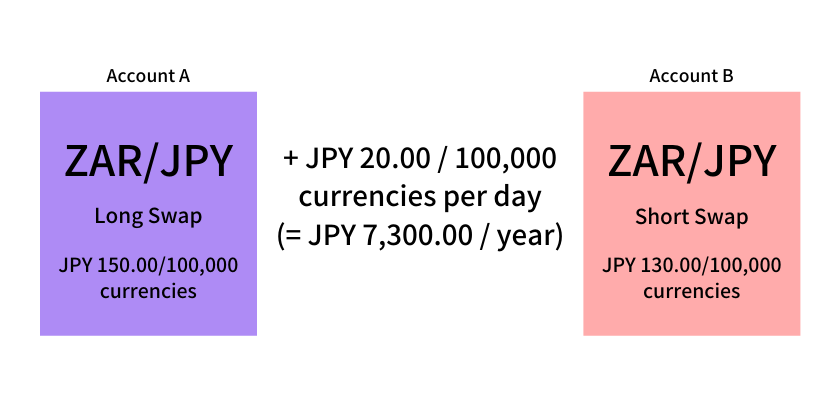
If a trader observes the inter-broker difference in swap points for the same currency pair to find the one preferable for the trader and does the transaction. In this case, the trader can theoretically eliminate the risk of exchange losses and earn profits.
[NOTE (ICYMI)]
THE ACTS MENTIONED ABOVE ARE ALL PROHIBITED BY MANY BROKERS.
DO NOT USE THESE PROCEDURES.
Penalty for Arbitrage
When an act of trading is determined as arbitrage, the broker penalizes the trader with the nullification of profits and the freeze on the acc. Please make sure to read through the terms and conditions of your broker for details.
How Brokers Detect Arbitrage
As mentioned repeatedly, arbitrage is illegal and a prohibited act. Nevertheless, some may assume that we can do the arbitrage as long as we can keep covering up it. But brokers can detect such an illegal act.
Trading Platform Keeps History of Transactions.
If a trader places cross orders through different brokers with the same trading platform, such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader5 (MT5), brokers can look over the history of transactions. The logic of how they keep track of it is not disclosed. But if there are multiple cross orders using different accounts, the broker will detect the act of arbitrage.
Identification from IP Address
A trader used another person’s account to place a cross order. However, as it was found that the trader had accessed the brokers’ servers from the same IP address, the trader’s act was deemed arbitrage.
Sharing The Same Server with Multiple Brokers
When a trader commits arbitrage with different brokers but the brokers share the same server or their servers are physically connected, the illegal act can be detected.
Conclusion
Finally, keep in mind that the following acts of trading fall under arbitrage which many brokers prohibit.
- Arbitrage taking advantage of bonus
- Arbitrage taking advantage of Negative Balance Protection
- Arbitrage taking advantage of swap points
What we should avoid is unintentional arbitrage. There is a possibility that, after a trader did a “legal” transaction, the act is later deemed arbitrage. Especially if you use multiple accounts to simultaneously manage various trading methods, these transactions may result in arbitrage as the cross order with multiple accounts.
Once again, the procedures introduced in this article are strictly prohibited. The purpose of this article is to introduce the prohibited acts as a reminder. Please kindly refer to this article and be careful not to conduct illegal transactions unintentionally.
Thank you for sparing your time to read this article.